

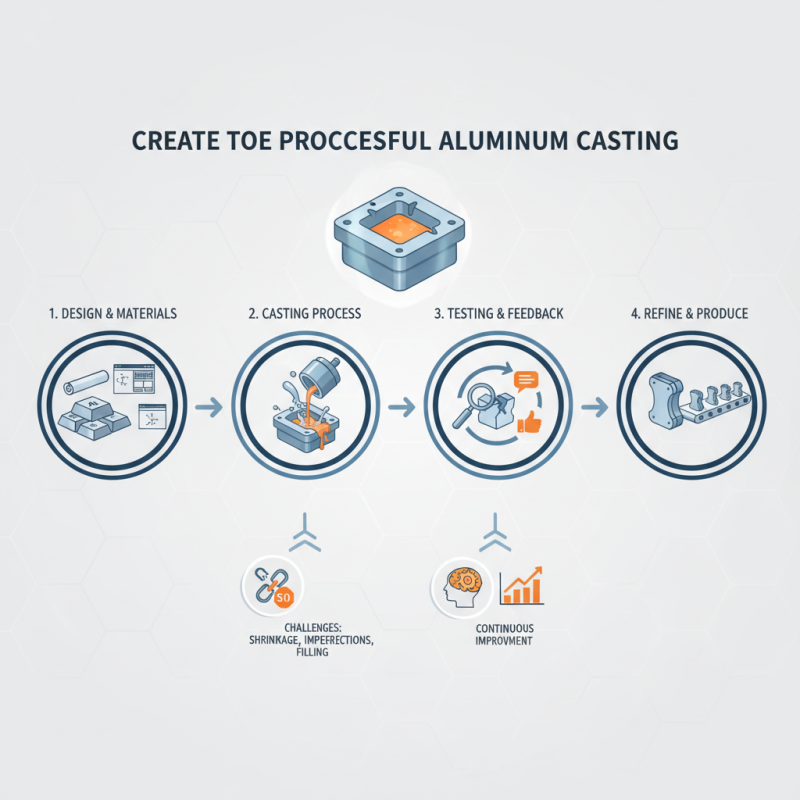
Creating a successful prototype aluminum casting process is crucial in many industries. This method allows engineers to develop products that meet specific design requirements. By using lightweight aluminum, manufacturers achieve enhanced performance and strength in their prototypes.
To build an effective prototype aluminum casting, one must consider several factors. The selection of materials, design complexity, and even the casting process itself play vital roles. Challenges often arise during prototyping. Issues such as shrinkage, surface imperfections, or inadequate mold filling can occur.
Attention to detail is necessary in every stage of the prototype aluminum casting process. Each cast must be reviewed for flaws. Feedback from the testing phase is invaluable. This step reinforces the importance of continuous improvement. A successful prototype will pave the way for larger production runs. Understanding and addressing the complexities of aluminum casting can lead to better outcomes.
Aluminum casting is a vital process in manufacturing. It offers various benefits, making it a popular choice for many industries. Lightweight yet strong, aluminum is ideal for creating complex shapes. This versatility plays a critical role in design efficiency.
Understanding the aluminum casting process is essential. Melted aluminum is poured into molds to form specific shapes. The cooling process is crucial. If cooled too quickly, cracks or defects may appear. Proper temperature management is necessary for quality outcomes. Each project requires careful planning to avoid such pitfalls.
Working with aluminum means embracing the need for precision. Each cast may reveal unexpected challenges. Surface imperfections might occur, or dimensions can be off. These factors demand reflection and adjustment in future prototypes. Identifying these issues early can save time and resources down the line. Embracing learning opportunities is crucial in achieving a successful aluminum casting process.
When embarking on a prototype aluminum casting project, selecting the right materials is crucial. Start with high-quality aluminum alloys. These alloys provide strength and durability. Common choices include 356 and 319 alloys. They offer good fluidity and are easy to cast. Ensure your aluminum is free from contamination. Even small impurities can affect the final product.
Molds play a pivotal role in the casting process. You can opt for sand molds or metal molds. Sand molds are versatile and cost-effective, but they may not deliver the best surface finish. Metal molds provide better precision but require higher initial investment. Consider the complexity of your design. If it has intricate features, a more precise mold will reduce the need for post-processing.
Additionally, don’t forget about the casting environment. A controlled temperature can make a difference. Too cold or too hot can lead to defects. Be prepared to adjust your setup based on your findings. Every casting process teaches you something new. Some experiments might not yield perfect results, but each step is a learning opportunity. Embrace the imperfections; they will guide you to improve.
Creating an aluminum prototype requires careful planning and execution. Start by defining your design specifications clearly. Sketch your ideas and make sure to include dimensions. Rely on CAD software to refine the designs. This step is crucial for accuracy. A well-defined design reduces errors later in the process.
Next, choose the right aluminum alloy for your prototype. Your choice can affect strength and ductility. Make sure to understand the properties of different alloys. This knowledge can save you time and resources. After selecting the alloy, prepare the mold. A poorly prepared mold can lead to flaws. Ensure surfaces are smooth and free from debris.
Once the mold is ready, it's time for pouring. Monitor the metal's temperature closely. Pour too hot, and you may have defects. Pour too cold, and you risk incomplete filling. After pouring, let the metal cool. This step is often rushed but essential for a quality finish. Afterward, inspect the prototype carefully for any imperfections. Adjust your process based on this feedback for continual improvement.

Aluminum casting presents various challenges that can impact the success of a prototype. One common issue is gas porosity. This occurs when gas gets trapped in the metal during cooling. Ample venting can mitigate this problem. Ensuring a clean mold surface is crucial as well. Any contamination can introduce gases, leading to defects.
Another frequent challenge is uneven cooling, which can weaken the final product. To address this, maintain consistent temperatures in the foundry. Using the right alloy also plays a significant role. Some alloys cool more uniformly than others. Adjusting the casting design to promote even flow can help too.
Sometimes, dimensional inaccuracies arise. This can stem from mold wear or miscalculations. Regularly checking and adjusting the mold helps ensure precision. It is essential to review the prototype after each run. Identifying flaws early can save time and resources later on. Prototyping demands a mix of careful planning and adaptability. Each iteration offers learning opportunities for improvement.

Testing and quality control are crucial in the prototype aluminum casting process. Ensuring that each prototype meets the desired specifications can save time and resources later on. Effective testing methodologies identify flaws early, allowing for adjustments before mass production.
Investing in detailed inspection techniques is vital. Utilize visual inspections for surface defects and non-destructive testing methods for internal integrity. Metrics such as dimensional accuracy and material properties should be consistently checked.
**Tips**: Always document your testing results. This creates a reference for future projects. Regularly review your quality control processes. Reflect on past prototypes to improve future iterations. Remember, perfection is a journey, not a destination. Embrace the learning curve and address the flaws. Each mistake is an opportunity for enhancement.






